BigArvin
Well-known member
Author
- Joined
- Aug 7, 2023
- Messages
- 158
- Points
- 28
Can something as tiny as a peptide influence medicine, personal care, and athletic performance? These microscopic molecules may revolutionize healthcare and fitness. Consisting of short sequences of amino acids, they exert a tremendous impact on science and health.
As we explore the realm of peptides, you'll learn that these microscopic molecules are largely unseen behind innumerable scientific advances. Let's dive straight into the world of peptides and explore their vital role in medicine, skincare, and sports.
View attachment 74907
A peptide bond is a covalent chemical bond between amino acids, also known as an amide bond, because of its chemical structure. It is responsible for the protein molecule's stability and folding into functional form. The peptide bond also influences the interactions between proteins and other molecules.
All living organisms contain peptides, including plants, animals, and bacteria. Hormones and neurotransmitters are molecules that convey signals between individuals.
A process called dehydration synthesis or condensation reaction forms peptide bonds. It removes water molecules during this reaction as two amino acids come together. One amino acid combines with another's carboxyl group, creating a peptide bond and a dipeptide molecule.
The sequence of amino acids along a peptide chain is of the utmost significance. This sequence determines a protein's primary structure, influencing how it pleats into its three-dimensional structure. A minor alteration in the line of amino acids can result in a substantial change in the system and process of a protein.
The amino acid sequence may also contribute to the protein's stability. Some sequences are more stable than others, and the stability of a peptide can impact its performance.
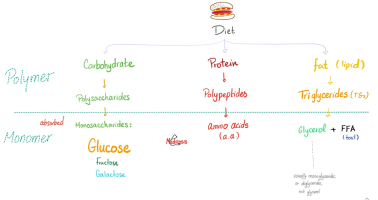
Peptides are brief amino acid chains, typically containing up to 50 amino acids. They are frequently signaling molecules or biological process intermediaries. Oxytocin and insulin are examples of hormones that regulate vital bodily functions.
Polypeptides are larger than peptides and can function as structural components in cells and tissues. They can range in length from dozens to hundreds of amino acids. Polypeptides are involved in several cellular processes, including DNA replication and protein synthesis. They also constitute the structural backbone of proteins.
Proteins are large, complex biomolecules composed of multiple polypeptide chains. They can range from hundreds to thousands of amino acid molecules. They are the largest of the three molecules and serve various purposes.
VIDEO about Peptides
The small size of peptides enables them to promptly navigate the complex pathways of life, rendering them indispensable to an individual's well-being. Understanding their diversity sheds light on the complexity of life at the molecular level.
Peptides also function as neurotransmitters, which are signal-carrying molecules between nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are released from the axon of one neuron and bind to dendritic receptors on another neuron. This binding induces an action in the second neuron, such as the discharge of an electrical signal.
Additionally, peptides possess antimicrobial activity, killing or inhibiting the proliferation of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. Antimicrobial peptides are molecules of the innate immune system that protect against various pathogens. They function as microbial guardians, disrupting pathogenic cell membranes and inhibiting growth.
Synthetic peptides have diverse applications in medicine, research, and cosmetics. They are customized for targeted functions like drug development and as research tools. Additionally, their bioavailability can vary based on their chemical structure and modifications.
Natural peptides occur naturally in living organisms. Living organisms generate them through genetic processes, obtainable from plants, animals, and bacteria. These peptides are often challenging to produce in large quantities and may contain impurities.
Synthetic and natural peptides rely heavily on their bioavailability for their efficacy. Peptides must reach their target tissues or cells to exert their functions. The body absorbs them and becomes available in the bloodstream for the intended physiological effect.
Scientists are creating peptide-based pharmaceuticals that selectively target cancer cells while minimizing unintended damage to healthy tissues. They deliver drugs to cancer cells to inhibit their growth and spread. Numerous cancer therapies based on peptides are currently undertaking clinical trials, offering hope for better outcomes.
Peptide-based insulin analogs provide more precise blood sugar control for individuals with diabetes. Glucagon-like peptides stimulate insulin secretion and reduce blood sugar levels. Current research seeks to develop innovative peptide-based therapies to manage diabetes more effectively.
Numerous factors influence the pharmacokinetics of peptides, including the peptide's size and structure, the route of administration, and the presence of enzymes that can degrade the peptide. However, challenges exist in delivering peptides orally due to digestive enzymes. They usually come in injections or intravenous methods for more reliable absorption.
Peptides can diminish the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, enhance skin texture, and even reduce skin sagging. They accomplish this by stimulating the production of collagen and elastin, the proteins responsible for the structure and elasticity of skin.
Skincare companies invest in advanced formulations and packaging to ensure the stability and longevity of peptides in their products. Peptides are available in numerous forms, such as serums, creams, and masks, impacting the peptides' stability.
Peptide-based supplements are gaining popularity among bodybuilders and athletes due to their capacity to promote muscle growth. They stimulate the release of growth hormone, which supports muscle protein synthesis and aids in the recovery of muscle tissues.
Peptides can improve athletic performance by increasing muscle strength, endurance, and power. Specific peptides, including Beta-Alanine and Creatine, improve muscle endurance by deferring fatigue during intense exercise. However, performance-enhancing peptides are subject to debate in sports due to concerns about fairness and safety.
Peptides are involved in hydrolysis during metabolism, breaking down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. Enzymes known as proteases facilitate hydrolysis. Proteases degrade peptides by cleaving the peptide bonds connecting the amino acids.
View attachment 74908
Some users may experience mild side effects like redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site when using peptide-based skincare products. These effects are usually temporary and subside within a few days.
Although rare, allergic reactions to peptides can cause hives, difficulty breathing, facial, lip, tongue, or throat puffiness. Any symptoms of an allergic reaction may necessitate prompt medical care. More adverse side effects are headaches, increased blood pressure, and anxiety.
Particularly in performance enhancement, excessive or improper use of peptides can adversely affect health. Some peptides are associated with more possible adverse effects than others. Before beginning treatment with a peptide, it is vital to consult your physician about any potential adverse effects.
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy published a journal in 2022 about the therapeutic applications of peptides. It said that produced and modified peptides using chemical and biological techniques have helped surmount the natural disadvantages of peptides in therapeutic applications. Aside from being drug carriers and vaccines, peptides can also exert anti-tumor effects.
A journal from Cambridge University Press also studied that collagen peptide can improve body composition and enhance muscle strength. It assessed the influence of collagen peptides on muscle mass after resistance training.
Insulin analogs, a form of peptide, are employed in treating diabetes. Cancer treatments based on peptides are also emerging as targeted therapies for specific cancer types. In this instance, the FDA regulates peptide-containing pharmaceuticals. Before approval, the FDA requires extensive clinical trials.
Peptide libraries are collections of thousands to millions of peptides synthesized for various applications. They are helpful for drug discovery, protein-protein interaction research, and vaccine development. By screening for peptides that interact with specific targets, libraries aid in identifying potential drug candidates.
Peptides can stimulate muscle protein synthesis, increasing muscle mass and strength. In addition, they stimulate the release of growth hormone, which contributes to muscle growth and repair.
Are there risks associated with peptide use?
Peptides can cause various side effects, including injection site reactions and allergies. However, some individuals may experience adverse side effects such as increased blood pressure, anxiety, and headaches.
How do chirality and isomers influence peptides?
Chirality and isomers significantly influence peptides' structure, properties, and biological activity. Chirality is a property that results from the spatial arrangement of atoms within a molecule, specifically around a chiral center. In contrast, isomers play an essential role in peptide synthesis, where specific diastereomers may help achieve desired chemical reactions.
Its future outlook in the medical field is also promising. They hold the potential for tailored treatments, addressing individual variations in health and genetics. Peptide research in sports science will likely expand, focusing on optimizing athletic performance safely and ethically.
As we explore the realm of peptides, you'll learn that these microscopic molecules are largely unseen behind innumerable scientific advances. Let's dive straight into the world of peptides and explore their vital role in medicine, skincare, and sports.
View attachment 74907
Definition of Peptides
A peptide is a short chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, ranging from a few to several dozen amino acids. There are 20 naturally occurring amino acids, each distinguished by its unique side chain. This diversity of side chains confers unique properties and functions to each amino acid.A peptide bond is a covalent chemical bond between amino acids, also known as an amide bond, because of its chemical structure. It is responsible for the protein molecule's stability and folding into functional form. The peptide bond also influences the interactions between proteins and other molecules.
All living organisms contain peptides, including plants, animals, and bacteria. Hormones and neurotransmitters are molecules that convey signals between individuals.
Amino Acids: The Building Blocks
Amino acids are organic molecules characterized by an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH). These compounds are the building elements of proteins and are essential to various biological processes.A process called dehydration synthesis or condensation reaction forms peptide bonds. It removes water molecules during this reaction as two amino acids come together. One amino acid combines with another's carboxyl group, creating a peptide bond and a dipeptide molecule.
The sequence of amino acids along a peptide chain is of the utmost significance. This sequence determines a protein's primary structure, influencing how it pleats into its three-dimensional structure. A minor alteration in the line of amino acids can result in a substantial change in the system and process of a protein.
The amino acid sequence may also contribute to the protein's stability. Some sequences are more stable than others, and the stability of a peptide can impact its performance.
Differentiating Between Peptides, Polypeptides, and Proteins
Biomolecules are intricate, with various compounds playing distinct roles in the functioning of living organisms. Among these, peptides, polypeptides, and proteins are critical actors with varying definitions, lengths, and complexity.Peptides are brief amino acid chains, typically containing up to 50 amino acids. They are frequently signaling molecules or biological process intermediaries. Oxytocin and insulin are examples of hormones that regulate vital bodily functions.
Polypeptides are larger than peptides and can function as structural components in cells and tissues. They can range in length from dozens to hundreds of amino acids. Polypeptides are involved in several cellular processes, including DNA replication and protein synthesis. They also constitute the structural backbone of proteins.
Proteins are large, complex biomolecules composed of multiple polypeptide chains. They can range from hundreds to thousands of amino acid molecules. They are the largest of the three molecules and serve various purposes.
VIDEO about Peptides
Types of Peptides
Peptides come in various forms, each with its unique purpose and function. They have diverse and vital roles in our bodies. Its most common types are:- Signaling Peptides: Signaling peptides are intracellular mediators that transmit information. The body uses them in numerous processes, including cell growth, immune responses, and metabolism. Hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors are three examples of signaling peptides. Insulin is also a signaling peptide that controls blood sugar levels.
- Carrier Peptides: Carrier peptides bond to and transport other molecules across cell membranes, ensuring they arrive at their intended destinations. They participate in numerous processes, including nutrient absorption, drug delivery, and immune function. Transferrin, which transports iron, and albumin, which transports proteins, are two examples of carrier peptides.
- Enzyme Inhibitors: Enzyme inhibitors are peptides that inhibit the activity of enzymes to regulate biochemical reactions. The body uses them to treat numerous diseases, including cancer and diabetes. They keep metabolic pathways in balance and prevent the overproduction of specific molecules. An example is protease inhibitors, which regulate digestion by inhibiting particular enzymes.
- Dipeptide, Tripeptide, Tetrapeptide: These peptides contain two, three, or four amino acids, respectively. They serve as building elements for longer peptides and proteins within the body. They contribute to various biological processes as intermediates to larger peptides and proteins. An example is glutathione, a tripeptide that acts as an antioxidant in the body.
The small size of peptides enables them to promptly navigate the complex pathways of life, rendering them indispensable to an individual's well-being. Understanding their diversity sheds light on the complexity of life at the molecular level.
Biological Functions
These molecular biomolecules are pivotal in coordinating various functions within our bodies. Peptides serve as crucial mediators in the endocrine system, regulating the production and release of hormones. They regulate numerous hormones, including insulin and vasopressin. Peptides also ensure the body's equilibrium by regulating growth, metabolism, and reproductive functions.Peptides also function as neurotransmitters, which are signal-carrying molecules between nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are released from the axon of one neuron and bind to dendritic receptors on another neuron. This binding induces an action in the second neuron, such as the discharge of an electrical signal.
Additionally, peptides possess antimicrobial activity, killing or inhibiting the proliferation of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. Antimicrobial peptides are molecules of the innate immune system that protect against various pathogens. They function as microbial guardians, disrupting pathogenic cell membranes and inhibiting growth.
Synthetic vs. Natural Peptides
Scientists create synthetic peptides in a laboratory using solid-phase peptide synthesis. This procedure involves one-by-one assembly of the intended sequence of amino acids. A laboratory can produce synthetic peptides in large quantities and with high purity. Scientists engineer them to possess specific sequences and properties unavailable in nature.Synthetic peptides have diverse applications in medicine, research, and cosmetics. They are customized for targeted functions like drug development and as research tools. Additionally, their bioavailability can vary based on their chemical structure and modifications.
Natural peptides occur naturally in living organisms. Living organisms generate them through genetic processes, obtainable from plants, animals, and bacteria. These peptides are often challenging to produce in large quantities and may contain impurities.
Synthetic and natural peptides rely heavily on their bioavailability for their efficacy. Peptides must reach their target tissues or cells to exert their functions. The body absorbs them and becomes available in the bloodstream for the intended physiological effect.
Therapeutic Uses
Peptides are making medical strides, particularly in treating a few chronic illnesses. It delivers drugs to specific cells or tissues and blocks the activity of enzymes or other molecules.Scientists are creating peptide-based pharmaceuticals that selectively target cancer cells while minimizing unintended damage to healthy tissues. They deliver drugs to cancer cells to inhibit their growth and spread. Numerous cancer therapies based on peptides are currently undertaking clinical trials, offering hope for better outcomes.
Peptide-based insulin analogs provide more precise blood sugar control for individuals with diabetes. Glucagon-like peptides stimulate insulin secretion and reduce blood sugar levels. Current research seeks to develop innovative peptide-based therapies to manage diabetes more effectively.
Numerous factors influence the pharmacokinetics of peptides, including the peptide's size and structure, the route of administration, and the presence of enzymes that can degrade the peptide. However, challenges exist in delivering peptides orally due to digestive enzymes. They usually come in injections or intravenous methods for more reliable absorption.
Skincare Benefits
Peptides offer a variety of skincare benefits, including anti-aging effects, skin-firming properties, and considerations regarding their stability in skincare products. They contribute to various skin functions, including the production of collagen and elastin, cell growth and repair, and wound healing.Peptides can diminish the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, enhance skin texture, and even reduce skin sagging. They accomplish this by stimulating the production of collagen and elastin, the proteins responsible for the structure and elasticity of skin.
Skincare companies invest in advanced formulations and packaging to ensure the stability and longevity of peptides in their products. Peptides are available in numerous forms, such as serums, creams, and masks, impacting the peptides' stability.
Sports and Fitness
Aside from the skincare and medical industries, peptides have also gained recognition for their diverse roles in muscle building, athletic performance enhancement, and digestion.Peptide-based supplements are gaining popularity among bodybuilders and athletes due to their capacity to promote muscle growth. They stimulate the release of growth hormone, which supports muscle protein synthesis and aids in the recovery of muscle tissues.
Peptides can improve athletic performance by increasing muscle strength, endurance, and power. Specific peptides, including Beta-Alanine and Creatine, improve muscle endurance by deferring fatigue during intense exercise. However, performance-enhancing peptides are subject to debate in sports due to concerns about fairness and safety.
Peptides are involved in hydrolysis during metabolism, breaking down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. Enzymes known as proteases facilitate hydrolysis. Proteases degrade peptides by cleaving the peptide bonds connecting the amino acids.
View attachment 74908
Safety and Side Effects
Peptides are safe for most individuals. However, there are a few potential adverse effects. The safety profile of a specific peptide will depend on the peptide, the dosage, and the administration route.Some users may experience mild side effects like redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site when using peptide-based skincare products. These effects are usually temporary and subside within a few days.
Although rare, allergic reactions to peptides can cause hives, difficulty breathing, facial, lip, tongue, or throat puffiness. Any symptoms of an allergic reaction may necessitate prompt medical care. More adverse side effects are headaches, increased blood pressure, and anxiety.
Particularly in performance enhancement, excessive or improper use of peptides can adversely affect health. Some peptides are associated with more possible adverse effects than others. Before beginning treatment with a peptide, it is vital to consult your physician about any potential adverse effects.
Research and Studies
Researchers have recently conducted several historical and contemporary scientific investigations on peptides. Most of these research studies hold promise for personalized medicine, increased precision, and diminished adverse effects.Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy published a journal in 2022 about the therapeutic applications of peptides. It said that produced and modified peptides using chemical and biological techniques have helped surmount the natural disadvantages of peptides in therapeutic applications. Aside from being drug carriers and vaccines, peptides can also exert anti-tumor effects.
A journal from Cambridge University Press also studied that collagen peptide can improve body composition and enhance muscle strength. It assessed the influence of collagen peptides on muscle mass after resistance training.
Commercial Products and Regulations
Many anti-aging serums now feature peptides like collagen-boosting palmitoyl pentapeptide or acetyl hexapeptide. Since these are cosmetic products, the FDA does not require approval before the manufacturer releases them. However, the FDA does have the authority to take action against skincare that are unsafe or that make false claims.Insulin analogs, a form of peptide, are employed in treating diabetes. Cancer treatments based on peptides are also emerging as targeted therapies for specific cancer types. In this instance, the FDA regulates peptide-containing pharmaceuticals. Before approval, the FDA requires extensive clinical trials.
Peptide libraries are collections of thousands to millions of peptides synthesized for various applications. They are helpful for drug discovery, protein-protein interaction research, and vaccine development. By screening for peptides that interact with specific targets, libraries aid in identifying potential drug candidates.
FAQs
Can peptides improve athletic performance?Peptides can stimulate muscle protein synthesis, increasing muscle mass and strength. In addition, they stimulate the release of growth hormone, which contributes to muscle growth and repair.
Are there risks associated with peptide use?
Peptides can cause various side effects, including injection site reactions and allergies. However, some individuals may experience adverse side effects such as increased blood pressure, anxiety, and headaches.
How do chirality and isomers influence peptides?
Chirality and isomers significantly influence peptides' structure, properties, and biological activity. Chirality is a property that results from the spatial arrangement of atoms within a molecule, specifically around a chiral center. In contrast, isomers play an essential role in peptide synthesis, where specific diastereomers may help achieve desired chemical reactions.
Conclusion
Peptides are short chains of amino acids, which are the fundamental building elements of proteins. Their compact size belies their importance in diverse biological functions. They have also gained popularity in sports and fitness because they stimulate muscle growth, improve endurance, and aid injury recovery. However, athletes should cautiously use them, considering safety, regulations, and individual differences.Its future outlook in the medical field is also promising. They hold the potential for tailored treatments, addressing individual variations in health and genetics. Peptide research in sports science will likely expand, focusing on optimizing athletic performance safely and ethically.